What is an Ozone Detector?
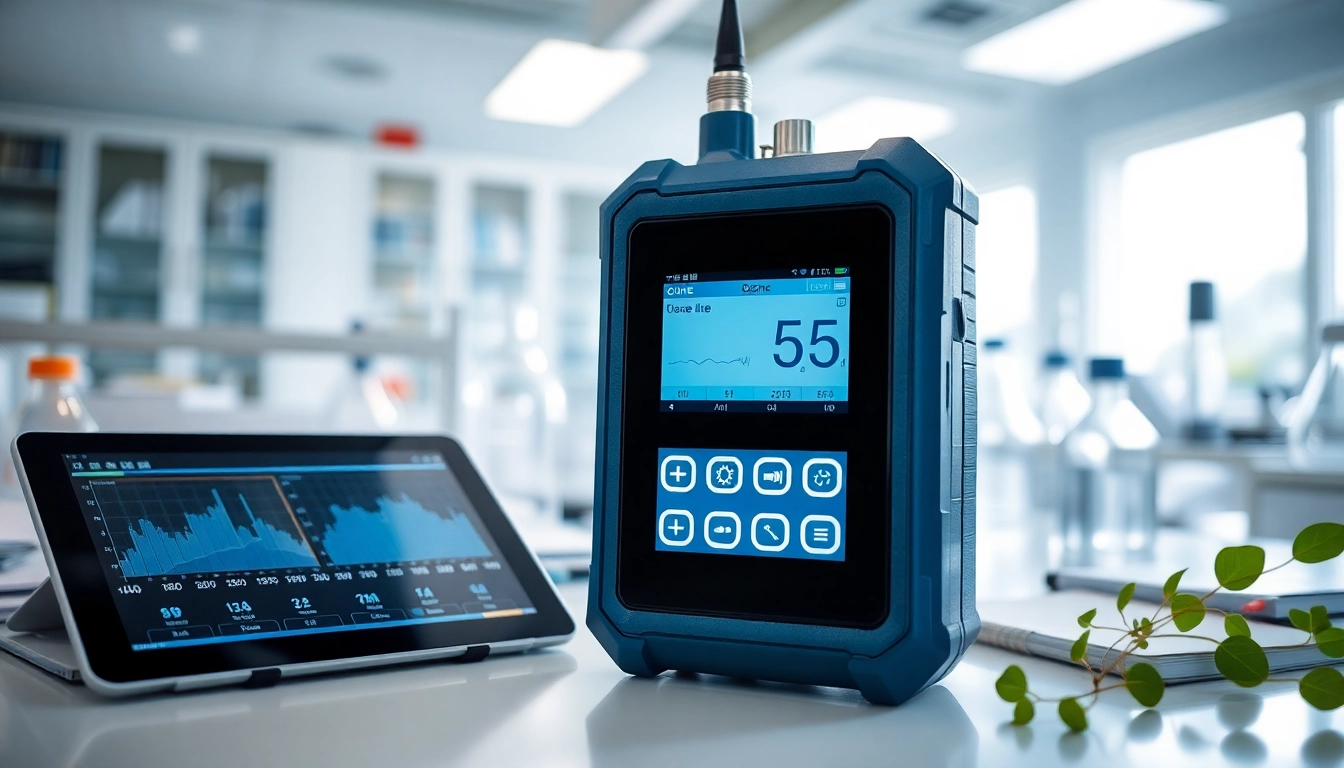
An ozone detector is a specialized instrument designed to measure and monitor the concentration of ozone (O3) in the air. Ozone is a triatomic molecule composed of three oxygen atoms and is present in both the Earth’s upper atmosphere and at ground level. While it’s beneficial in the upper atmosphere for absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation, at ground level, it poses health risks and environmental concerns. Industries such as manufacturing, environmental monitoring, and health sectors rely heavily on accurate ozone detection for safety compliance and air quality management. For more details, explore our ozone detector offerings.
The Science Behind Ozone Detection
The ability to detect ozone concentrations relies on various scientific principles, particularly those associated with its unique chemical properties. Ozone is a strong oxidant, which allows it to react with other compounds in the air. Detection methods typically hinge on the adsorption of ozone molecules onto a sensor surface, leading to measurable electronic changes.
Common detection techniques include:
- Electrochemical sensors: These sensors use chemical reactions that occur at the electrode surface to produce a measurable electrical current proportional to the ozone concentration.
- UV photometry: This method involves exposing ambient air to UV light, where ozone absorbs specific wavelengths, allowing for concentration calculations based on the amount of light absorbed.
- Metal oxide semiconductors (MOS): In these systems, ozone interacts with a metal oxide surface, changing the resistance of the sensor, which can be quantitatively measured.
Types of Ozone Detectors Available
Ozone detectors are available in various types, catering to different industrial needs and detection environments:
- Portable ozone detectors: Compact and battery-operated, these are ideal for fieldwork and personal safety monitoring, providing real-time readings and alerts.
- Fixed ozone detectors: Designed for continuous monitoring in a specific location, these devices offer long-term data collection, often integrated with alarm systems for hazardous situations.
- Integrated systems: These advanced units often come with multiple sensing technologies, allowing for comprehensive air quality management and reporting features.
How Ozone Detectors Work
The functionality of ozone detectors hinges on the specific technologies they employ. An electrochemical sensor, for example, operates through oxidation-reduction reactions when ozone penetrates the sensor membranes. The produced current correlates with the ozone molecule concentration.
In contrast, UV photometric sensors measure the specific decrease in UV light intensity as it passes through an air sample. This method is very precise, allowing for detection in environments with varying levels of interference from other airborne substances.
Importance of Ozone Detectors in Various Industries
Ozone detectors play a critical role across different industries, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and improving health outcomes. Their importance can be observed in various applications:
Ozone Detectors in Environmental Monitoring
Environmental monitoring programs utilize ozone detectors to ensure that air quality standards are met. Given that ground-level ozone can cause respiratory issues and other health problems, continuous monitoring is vital. Detection data assists in understanding pollution sources, guiding remediation strategies, and supporting legislative compliance regarding air quality regulations.
Governments and environmental organizations employ networks of ozone sensors to gain insight into urban air quality, enabling timely alerts for high ozone days and pollutant tracking.
Ozone Detection in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, ozone is often used in processes like water treatment and paper bleaching. However, high concentrations can pose health risks to workers. Hence, factories must monitor ozone levels to protect their employees and comply with OSHA regulations. Implementing ozone detectors in strategic locations helps mitigate risks, leading to a safer working environment.
Additionally, some manufacturing processes use ozone for its antimicrobial properties. Understanding ozone levels ensures effectiveness while minimizing health hazards.
Health and Safety Applications of Ozone Detectors
Health facilities and laboratories utilize ozone detectors to monitor air quality closely. In environments where ozone is used for sterilization or disinfection, it’s crucial to maintain safe levels to prevent harm to staff and patients. Accurate measurement and alert systems help ensure that ozone concentrations remain within safe thresholds.
Furthermore, industrial hygiene professionals may use these detectors to conduct risk assessments, ensuring that compliance with safety standards is met continually.
Choosing the Right Ozone Detector for Your Needs
When selecting an ozone detector, understanding specific needs and application environments is critical. Several factors influence the choice of an appropriate detection device.
Key Features to Consider
Several features should be considered when evaluating ozone detectors:
- Detection range: The required range varies based on the specific application. Some environments may necessitate low-level detection, whereas industrial applications could require higher sensitivity.
- Response time: Time taken to achieve stable measurements should be quick, especially in environments that may experience sudden ozone fluctuations.
- Data output and connectivity: Consider whether the device offers integration with data logging and reporting systems for compliance tracking and analysis.
- Calibration and maintenance needs: Opt for models that allow easy calibration and come with a clear maintenance schedule to ensure reliability.
Comparing Ozone Detector Brands and Models
Numerous brands exist in the ozone detector market, each offering various features and specialties. When comparing models, consider:
- Price Point: Budget considerations are crucial, but ensure that the chosen model also aligns with required features.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Peer recommendations can provide insight into the reliability and effectiveness of specific models.
- Warranty and Support: Check warranty offerings and customer support levels, which can significantly influence long-term satisfaction.
Budgeting for Your Ozone Detection Solutions
Developing a budget for ozone detection solutions involves considering both initial investment and ongoing operational costs. Factors influencing budgeting include:
- Initial Purchase Cost: Research various models and their prices, understanding the balance between price and necessary features.
- Maintenance Costs: Consider costs for calibration, regular testing, and potential repairs.
- Training Expenses: If the device requires specialized knowledge, budget for training personnel on proper use and maintenance.
Installation and Maintenance of Ozone Detectors
Once a suitable ozone detector has been selected, correct installation and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Below is a guide on proper procedures.
Steps to Properly Install an Ozone Detector
Installation procedures may vary depending on the type of detector chosen. However, general steps often include:
- Choose Strategic Locations: Install detectors where ozone levels are likely to fluctuate or where potential risks are high.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Detailed installation instructions are typically provided by manufacturers and should be strictly followed.
- Ensure Proper Power Supply: Check that the device has a reliable power source or battery backup if needed.
- Connectivity Setup: If applicable, establish connections to data logging and alarm systems to facilitate real-time monitoring and alerts.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Ozone detectors require regular maintenance to function correctly, which includes:
- Routine Calibration: Calibrate sensors based on manufacturer recommendations, often involving specialized calibration gases.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Periodically check for damage to sensors or electrical components, replacing any faulty parts.
- Software Updates: Update software for models with integrated systems, ensuring all features function optimally.
Troubleshooting Common Ozone Detector Issues
Even with diligent maintenance, issues may arise with ozone detectors. Common problems include:
- False Readings: This can occur due to sensor drift or interference from other gases. Regular calibration can help mitigate this.
- Power Supply Issues: Check for connection problems or battery failures. Installing a backup power supply is advisable.
- Inability to Connect to Data Systems: Ensure that network settings are configured correctly and check for software updates or compatibility issues.
Analyzing Ozone Detection Data for Improved Safety
The effectiveness of ozone detectors lies in their data outputs. Understanding and analyzing this data can enhance safety protocols, compliance with regulations, and overall air quality management.
Interpreting Ozone Measurement Readings
Understanding ozone readings can inform health safety decisions and environmental actions. The measurements typically indicate parts per million (ppm) or micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3). Knowing the safe ozone levels according to environmental regulations is essential for interpretation.
The typical threshold for ozone exposure varies, with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishing health standards based on average exposure times.
Utilizing Data for Compliance and Reporting
Diligently logging and interpreting detection data enables compliance with local and national air quality regulations. Use this data for:
- Regulatory Reporting: Many jurisdictions require regular reporting on air quality data, often mandating ozone levels specifically.
- Risk Assessment: Analyze historical data for patterns in ozone levels, enabling better risk assessments for occupational health and safety programs.
- Public Safety Notifications: When levels exceed safety thresholds, timely alerts and notifications to the public are critical.
Improving Air Quality Management with Ozone Data
Data from ozone detection not only supports compliance but can also drive effective strategies for improving air quality management. Stakeholders can utilize this data to:
- Identify Pollution Sources: Continuous monitoring can highlight areas with persistent ozone levels, potentially tied to specific industries or traffic patterns.
- Implement Proactive Measures: Ozone data can inform interventions, including regulatory changes, public awareness campaigns, and further investments in green technologies.
- Enhance Community Health Initiatives: By understanding ozone exposure levels, agencies can develop health initiatives targeting vulnerable populations equally.